
Semiconductor detectors make it possible to measure the separate probabilities for Rayleigh and Compton scattering. The development of high-resolution silicon and germanium semiconductor radiation detectors opened new areas for applications of Compton scattering. In addition the Compton effect provides an important research tool in some branches of medicine, in molecular chemistry and solid-state physics, and in the use of high-energy electron accelerators and charged-particle storage rings. Compton scattering (often referred to as incoherent scattering, in contrast to Thomson scattering or also Rayleigh scattering, which are called coherent scattering) is important in nuclear engineering (radiation shielding), experimental and theoretical nuclear physics, atomic physics, plasma physics, x-ray crystalloghaphy, elementary particle physics, and astrophysics, to mention some of these areas. The Compton effect has played a significant role in several diverse scientific areas. Schrödinger and provided the basis for the beginning of the theory of quantum electrodynamics, the theory of the interactions of electrons with the electromagnetic field. Debye led to the formulation of quantum mechanics by W. Perhaps the greatest significance of the Compton effect is that it demonstrates directly and clearly that in addition to its wave nature with transverse oscillations, electromagnetic radiation has a particle nature and that these particles, the photons, behave quite like material particles in collisions with electrons. See Angular momentum, Atomic structure and spectra, Electron-positron pair production, Light, Photoemission, Quantum mechanics, Uncertainty principle Together with the laws of atomic spectra, the photoelectric effect, and pair production, the Compton effect has provided the experimental basis for the quantum theory of electromagnetic radiation. The Compton effect illustrates one of the most fundamental interactions between radiation and matter and displays in a very graphic way the true quantum nature of electromagnetic radiation. This increase in wavelength is caused by the interaction of the radiation with the weakly bound electrons in the matter in which the scattering takes place. The increase in wavelength of electromagnetic radiation, observed mainly in the x-ray and gamma-ray region, on being scattered by material objects.
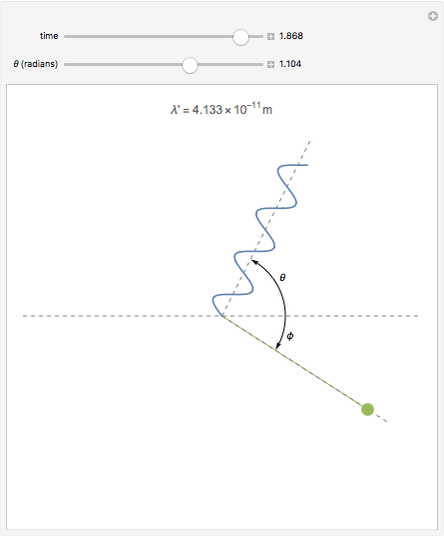
The Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia™ Copyright © 2022, Columbia University Press. It is used in the study of electrons in matter and in the production of variable energy gamma-ray beams. A larger scattering angle will yield a larger increase in wavelength. It depends only upon the angle that is formed between the incident and scattered rays.

The increase in the wavelength does not depend upon the wavelength of the incident rays or upon the target material. Since the energy and magnitude of linear momentum of a photon are proportional to its frequency, after the collision the photon has a lower frequency and thus a longer wavelength. According to the quantum theory a photon can transfer part of its energy and linear momentum to a loosely bound electron in a collision. The classical treatment of these rays as waves would predict no such effect.
#GRAPH COMPTON EFFECT VERIFICATION#
This effect provides strong verification of the quantum theory since the theoretical explanation of the effect requires that one treat the X rays and gamma rays as particles or photons (quanta of energy) rather than as waves. Compton effect, increase in the wavelengths of X rays and gamma rays when they collide with and are scattered from loosely bound electrons in matter.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
